Instances
Introduction
Kianda’s REST Application Programming Interface (API) for instances allows you to flexibly and efficiently perform database operations or methods such as create, update and get/retrieve values on process instances. A process instance is created every time data is either saved or submitted to Kianda’s database for a given process design, see Process instance for more details.
How to get started
Before you get started, there are three things to keep in mind:
-
To use API methods in Kianda you must have an administrator role, go to View and edit user details to see information on how to set roles.
-
Each API method requires a Bearer token, see Authentication for more details.
-
Each of the following methods can be used on process instances or records, where {name} is the name of a process instance, such as ’training-approval-request-1'.
REST API Methods
You can perform Create, Read, and Update operations on Kianda resources using standard HTTP method requests, as summarised below:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| POST | Create a process instance |
| GET | Read/Retrieve process instance fields |
| PUT | Update a process instance |
| PATCH | Partially update a process instance |
Before any of the requests are used, you must have the bearer access token inserted into the request header, see Authentication for details.
Create a process instance - POST
This request creates a process instance/new record. To use POST:
- Use the following request format:
{{domain}}/api/instances/create
-
Ensure that the bearer token is inserted into the authorisation header
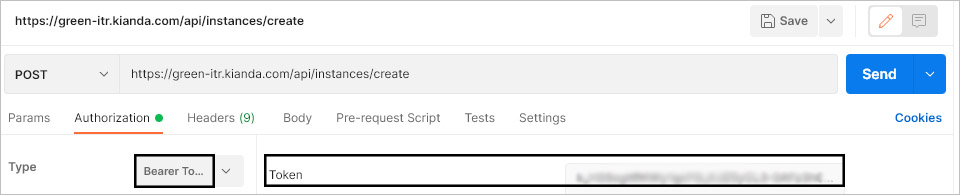
-
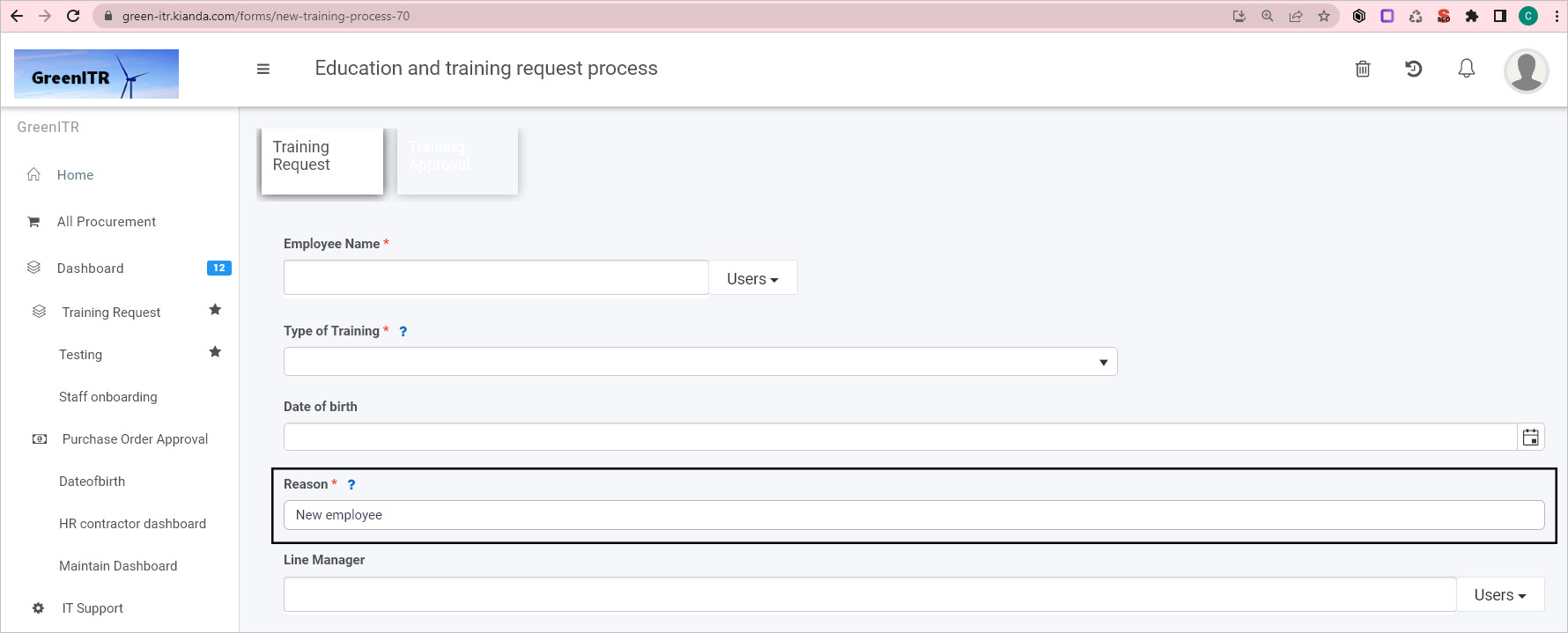
Pass parameters into the body of the request, for example to create a new instance of a process called ’new-training-process’ where a textbox field called ‘Reason’ will be prepopulated with a value:
{ "processName" :"new-training-process", "instanceID" : "new-training-process", "TriggerField":"", "FieldsMappings":[{ "fieldname":"reason", "text":"New employee", "value":"New employee" } ] } -
The Response Body will be as follows:
{
"success":true,
"instanceID":"new-training-process-70"
}
In the example above a new instance is created with an ID ’new-training-process-70’. The new instance can be see in a List widget in a dashboard as follows.
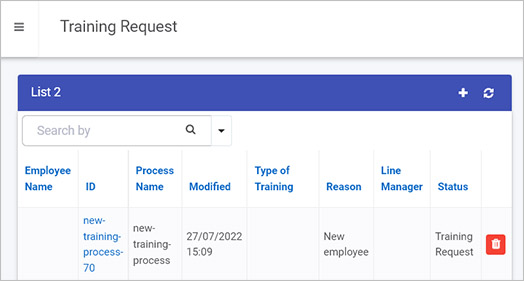
In this example the Reason text box is populated from the POST request.
Read/Retrieve process instance fields - GET
{{domain}}/api/instances/{name}/fields?names=field1,field2..
where `{name}`is the name of the process instance.
This request retrieves the values of multiple fields by name.
No Request Body is required.
The Response Body will be as follows:
{
"name":"",
"text":"",
"value":"",
}
Update a process instance - PUT
{{domain}}/api/instances/{name}
where `{name}`is the name of the process instance.
This request updates all fields in the instance by performing a comparison based on version number, to ensure there are no duplicate process instances.
The Request Body for the PUT request is:
{
"ProcessName":"",
"FieldsMappings":[],
"TriggerField":"",
"Status":""
}
The Response Body will be as follows:
{
"ProcessName":"",
"FieldsMappings":[],
"TriggerField":"",
"Status":""
}